TAPVC, or Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection is a defect in the venous flow from the lungs to the heart, allowing the mixing of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood. This condition is diagnosed early in life by Cardiologist in Lahore and is often accompanied by other defects, as well. Read on to know more about TAPVC:
What is TAPVC?
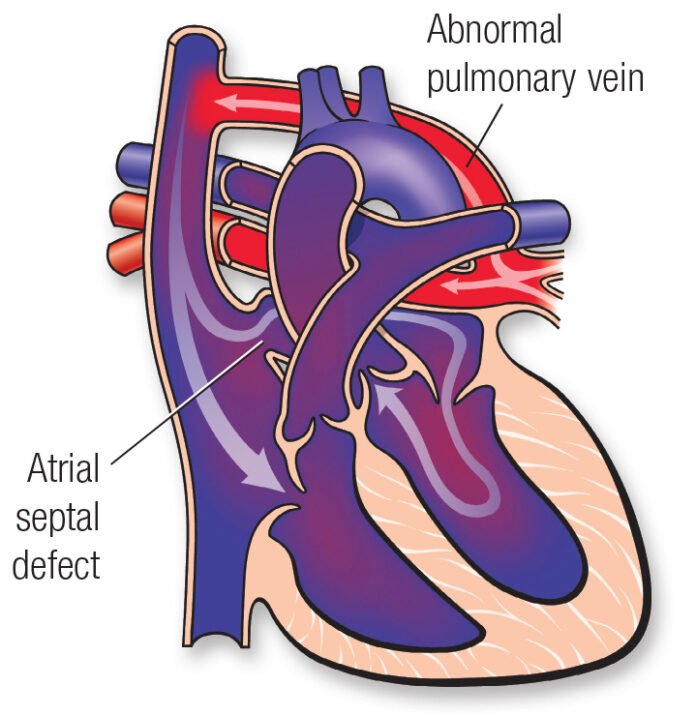
In the birth defect of TAPVC, the blood returning from the lungs to the heart via the pulmonary veins, does not attach to the left atrium of the heart. Instead, the pulmonary vein comes with oxygenated blood to the right side of the heart, where normally the deoxygenated blood is present. Thus, there is mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood and the baby gets less oxygen than normal. With TAPVC, there are often concurrent defects like atrial septal defects (ASD), which allow survival by mixing of blood.
In normal conditions, the pulmonary veins bring oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left side of the heart, and through the aorta to the rest of the body; while the inferior and superior vena cava bring deoxygenated blood back from the body to the right side of the heart.
Babies born with this defect need surgical repair as soon as possible, after birth.
What are the types of TAPVC?
There are different types of TAPVC, including:
- Supra-cardiac: in this type of TAPVC, the pulmonary veins form an abnormal connection with the superior vena cava (SVC), above the heart. The SVC, is the vessel that brings deoxygenated blood from the head and neck, back to the right chamber of the heart. Consequently, there is mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood that ends up in the right heart.
- Infra-cardiac: as the name implies, this is the type of TAPVC, in which the pulmonary veins form abnormal connection below the heart, with the inferior vena cava (IVC). The IVC brings the deoxygenated blood back from the body to the right heart. Again, there is mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- Cardiac: in this type of TAPVC, the pulmonary veins coalesce behind the heart and connect to the right atrium.
What are the symptoms of TAPVC?
The symptoms of TAPVC in the infants include:
- Weak pulse
- Breathing problems
- Poor feeding
- Bluish discoloration of skin
- Pounding heart
- Extreme lethargy
- Murmurs
How is TAPVC diagnosed?
The diagnosis of TAPVC is based on thorough history and physical examination, followed by investigations like:
- Blood tests like pulse oximetry: sense the oxygen levels in the body
- Electrocardiography: ECG changes are seen in TAPVC patients
- Chest x-ray: with TAPVC, there is obstruction in the pulmonary blood vessels and these changes reflect on the chest x-ray.
- Angiography: detailed flow of blood is found with this test.
- Echocardiography: this test uses sound waves to create images of heart in motion.
- MRI: images of the heart are created with cardiac MRI.
What are the treatment options?
The ultimate option for TAPVC treatment is surgical repair. The right time of surgery for the baby depends on the severity of illness and presence of concurrent defects. The goal of surgery in TAPVC, is to redirect the blood flow to the left heart completely and to close septal defects.
Along with surgical repair, medication to control the symptoms include: blood pressure drugs, anti-arrhythmic drugs and diuretics to reduce the strain on heart.
What are the risks of TAPVC surgery for the baby?
As with every type of surgery there are some risk factors associated and complications can develop. These may include:
- Infection
- Excessive bleeding
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Heart block
- Anesthesia complications
- Blood clot
- Death
What are the long-term outcomes of TAPVC?
The long-term outlook for TAPVC is excellent. Most patients with TAPVC get surgery in childhood; adults with this disorder are also eligible for surgery later on. Even after surgical repair, periodic checkup with Cardiologist in Rawalpindi is needed to avoid uncommon problems. The medical follow-up can also include non-invasive investigations like echocardiogram, stress test, Holter monitoring and electrocardiogram.
Also Read: Optimal Window Solutions with Exemplary Range of Curtains & Blinds in Melbourne.