Heat exchangers have a broad range of uses in industrial process engineering. A manufacturing company uses heat exchangers in manufacturing various products to exchange heat from one fluid to another.
A wide range of applications for heat exchangers includes those used in homes, environments and industries with different temperature requirements. To learn about the applications of heat exchangers in detail, we need an overview of what heat exchangers are and their types.
Meaning of Heat Exchangers
A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between two fluids that are not in direct physical contact. A heat exchanger is helpful as it allows one of the fluids to be heated or cooled without requiring any actual movement of that fluid.
Types of Heat Exchangers
Several types of heat exchangers are available in the market for various applications. Some of them are discussed below:
Tube in Tube Heat Exchangers
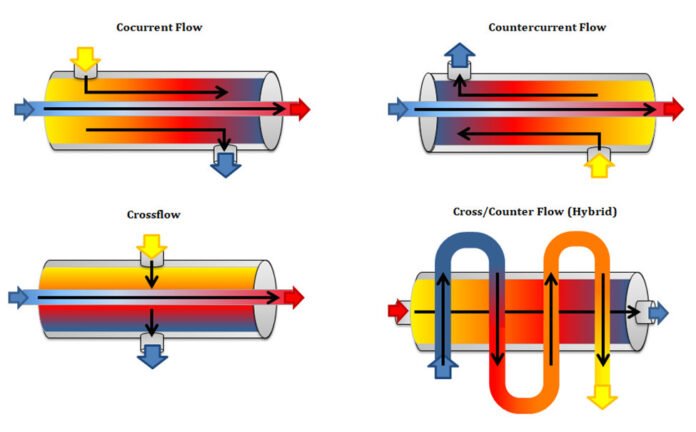
A tube heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger where the tubes are parallel, and the cross-flow from one side to another is blocked using baffles or blocks.
Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are made up of thin sheets or plates connected by flanges and seals. The advantages include good temperature uniformity, high efficiency and good corrosion resistance.
Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
This type of heat exchanger is made up of two pipes which are connected. The pipes are sealed at both ends to prevent any leakage of fluid.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
This heat exchanger consists of a cylindrical shell, called the shell, and a tube-like element, called an expansion vessel. The cylindrical shell design aims to reduce overall system resistance and improve efficiency by allowing for more rapid expansion and contraction between hot and cold fluids within the same system.
Applications of Heat Exchangers
In manufacturing heat exchangers, there are different applications that you can use them for. Here are the eight main ones:
1. Condensers
Condensers are used to cool the vapour from a liquid. The vapour condenses on the inside walls of the condenser and then flows back through the condenser into the original liquid or gas stream. As it cools, it must be condensed using a cooling coil, which uses energy to evaporate water from the surrounding air, turning it into steam. It then cools down even more and returns as low-pressure steam through an economiser to drive additional power production equipment.
2. Coolers
Coolers are another common application for heat exchangers. They are used to cool liquids and gases. The cooling process is used in many industries, such as the food and beverage industry, the pharmaceutical industry, food manufacturing companies and the electronics industry. Coolers are also used in air conditioners and refrigerators.
3. Evaporators
Evaporative cooling is used to cool industrial processes and air conditioning systems. The process relies on moisture absorption by water or other liquids at ambient temperatures, which results in a moderate degree of cooling. Evaporators can also be used to distil a liquid by heating the liquid and then allowing it to evaporate. The evaporator then collects the vapour and condenses it into liquid form. Heat exchangers for evaporation are used in various industries, including HVAC, refrigeration, and chemical processing.
4. Reboilers
Reboilers typically have one or more tubes that run through them. Tubes are filled with the heated liquid, and then the hot fluid transfers its heat to the liquid in the pipes and is heated to the desired temperature. Reboilers are an essential piece of equipment in many industries. Reboilers are used in many processes, such as distillation, extraction, and fractional crystallisation. They also heat liquids to their boiling point so they can be evaporated or distilled.
5. Chillers
The chiller works by moving large amounts of liquid through pipes at low pressure, thereby cooling down the liquid faster at higher temperatures lower than those existing outside pipes. Chillers are commonly used in air conditioning systems and help to keep the air inside a building cool and comfortable. Chillers are also used in refrigeration systems to keep food and other perishable items fresh and free from spoilage.
6. Vaporisers
Vaporisers are heat exchangers used to heat fluids to their boiling point. Vaporisers can be used for various applications, including heating water for domestic use, heating oil for industrial use, and even vaporising liquid nitrogen. Vaporisers work by passing a hot fluid (such as steam) through a series of tubes. The fluid transfers its heat to the tubes, which heats the liquid inside them. It causes the fluid to reach its boiling point and turn into vapour.
7. Oil cooling
Oil cooling is when heat exchangers remove heat from the oil. It is done by circulating oil through a heat exchanger or by using a heat exchanger to cool oil that another process has heated. Using heat exchangers in oil refineries and petrochemical plants is a common practice. In refining, crude oil is heated and transported to a distillation column, separated into various fractions and products. The hot, vaporised product then travels to a condenser where water and other materials are separated from it.
8. Double Pipe Exchangers
Double pipe exchangers consist of two pipes with different diameters connected with a tight-fitting connector. A double pipe heat exchanger works well when there are significant differences between the temperatures of hot and cold fluids. For instance, in an oil refinery where there is a substantial difference between the temperature of steam coming out of the boiler and the temperature of condensate coming out of condensation towers.
The heat exchanger is a device that can transfer heat from one kind of fluid into another fluid. Depending upon the application of the heat exchanger, the manufacturer also designs a heat exchanger accordingly. When manufacturing heat exchangers, you need to know that different heat exchanger sizes are used during various applications.